


Next: ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Up: DISCOVERING PREDICTABLE CLASSIFICATIONS (Neural
Previous: FINDING PREDICTABLE DISTRIBUTED REPRESENTATIONS
In contrast to the principled approach embodied by IMAX,
our methods (1) tend to be simpler (e.g., do not require sequential
layer by layer `bootstrapping' or learning rate adjustments -
the stereo task can be solved more readily by our system),
(2) do not require Gaussian assumptions about the input or output signals,
(3) do not require something like 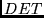 MAX,
(4) partly have (unlike
MAX,
(4) partly have (unlike 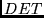 MAX) a potential for creating
classifications with statistically independent components (this
holds for
MAX) a potential for creating
classifications with statistically independent components (this
holds for  defined according to section 2.4).
In addition, our approach makes it easier to decide whether
the outputs of both networks essentially represent the same thing.
defined according to section 2.4).
In addition, our approach makes it easier to decide whether
the outputs of both networks essentially represent the same thing.
The experiments above show that the alternative methods
of section 2 can be useful for
implementing the  terms in (4) to obtain
predictable informative input transformations.
More experiments are needed, however, to become clear about their
mutual advantages and disadvantages.
It also remains to be seen how well the methods of this paper
scale to larger problems.
terms in (4) to obtain
predictable informative input transformations.
More experiments are needed, however, to become clear about their
mutual advantages and disadvantages.
It also remains to be seen how well the methods of this paper
scale to larger problems.
Juergen Schmidhuber
2003-02-13
![]() terms in (4) to obtain
predictable informative input transformations.
More experiments are needed, however, to become clear about their
mutual advantages and disadvantages.
It also remains to be seen how well the methods of this paper
scale to larger problems.
terms in (4) to obtain
predictable informative input transformations.
More experiments are needed, however, to become clear about their
mutual advantages and disadvantages.
It also remains to be seen how well the methods of this paper
scale to larger problems.