


Next: A DISADVANTAGE OF THE
Up: OBJECTIVE FUNCTIONS FOR THE
Previous: REMOVING THE VARIANCE TERM:
Theoretically it is sufficient to do without the auto encoder
and set 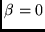 in (4). In this case, we simply
want to maximize
in (4). In this case, we simply
want to maximize
The 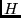 -Term counteracts
the possibility that different (near-) binary units convey
the same information about the input.
Setting
-Term counteracts
the possibility that different (near-) binary units convey
the same information about the input.
Setting 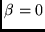 means to maximize information
locally for each unit while at the same time trying to
force each unit to focus on different pieces of information
from the environment.
Unlike with auto-associators,
there is no global invertibility term.
means to maximize information
locally for each unit while at the same time trying to
force each unit to focus on different pieces of information
from the environment.
Unlike with auto-associators,
there is no global invertibility term.
Note that this method seemingly works diametrically opposite to
the sequential, heuristic, non-neural methods described
by Barlow et al. (1989), where
the sum of bit entropies is minimized instead of
being maximized. How can both methods pursue the same goal?
One may put it this way: Among all invertible codes,
Barlow et. al. try to find those closest to something
similar to the independence
criterion.
In contrast, among all codes fulfilling the independence
criterion (ensured by sufficiently strong 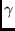 ),
the above methods try to find the invertible ones.
),
the above methods try to find the invertible ones.



Next: A DISADVANTAGE OF THE
Up: OBJECTIVE FUNCTIONS FOR THE
Previous: REMOVING THE VARIANCE TERM:
Juergen Schmidhuber
2003-02-13
Back to Independent Component Analysis page.
![]() ),
the above methods try to find the invertible ones.
),
the above methods try to find the invertible ones.